Outline of the human brain
Overview of and topical guide to the human brain
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human brain:
Structure of the human brain
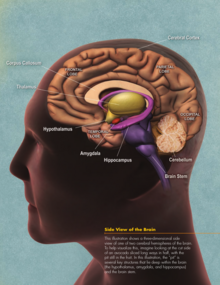
Visible anatomy
- Human brain – central organ of the nervous system located in the head of a human being
- Neuroanatomy
- Regions in the human brain:
- Cerebrum
- Cerebral cortex
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Occipital lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Limbic lobe
- Hippocampus
- Basal ganglia
- Cerebral cortex
- Cerebellum
- Hypothalamus
- Amygdala
- Brain stem
- Medulla oblongata
- Midbrain
- Pons
- Cerebrum
- Significant components:
- Arcuate fasciculus – neural pathway connecting the junction between the temporal and parietal lobes with the frontal cortex in the brain
- Broca's area – region of the brain with functions linked to speech production
- Triangular part of inferior frontal gyrus – part of Broca's area that contributes to propositional (true/false) language comprehension
- Caudate nucleus – located within the basal ganglia and involved in learning and memory
- Central nucleus of the amygdala – the major output nucleus of the amygdala, participates in receiving and processing pain information
- Nucleus accumbens – collection of neurons in the pleasure center that is thought to play a role in reward, pleasure, laughter, addiction, aggression, fear, and the placebo effect
- Pineal gland – a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain that produces melatonin, a hormone that affects wake/sleep patterns
- Ventricular system – set of structures containing cerebrospinal fluid which bathes and cushions the brain and spinal cord within the skull
- Cranial nerve – neuron bundles that connect to the brain on one end, and to locations outside the brain on the other, without having a junction inside the spinal column
- Cranial nerve zero – controversial but commonly found nerve which may be vestigial or may be related to sensing pheromones
- Olfactory nerve (cranial nerve 1) – smell
- Optic nerve (cranial nerve 2) – sight
- Oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve 3) – eye movement (except rotation)
- Trochlear nerve (cranial nerve 4) – eye rotation
- Trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve 5) – sensation from the face and certain motor functions such as biting and chewing
- Abducens nerve (cranial nerve 6) – certain eye rotation
- Facial nerve (cranial nerve 7) – facial expression and taste sensations from the tongue
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve 8) – hearing and balance
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve 9) – sensation from the throat, tonsils, part of the tongue, heart, and stomach. Also facilitates swallowing.
- Vagus nerve (cranial nerve 10) – output to the intestines and heart, taste information, deep/crude touch, pain, temperature of outer ear
- Accessory nerve (cranial nerve 11) – specific muscles of the shoulder and neck. Modern descriptions often consider the cranial component as part of the vagus nerve, calling what is left the spinal accessory nerve.
- Hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve 12) – muscles of the tongue
- Spinal cord – bundle of neurons that connects the brain to the peripheral nervous system and coordinates certain automatic reflexes
- Peripheral nervous system – nerves outside the brain and spinal cord
Microscopic level anatomy
- Neuron – electrically excitable cells that make up the brain
- Synapse
- Neural network
- Nervous tissue
- Cytochrome c oxidase – correlated with neuronal activity, and used for mapping regional brain metabolism in animals
- Electromagnetic theories of consciousness – the theory that consciousness is located in the brain's electromagnetic field rather than inside the neurons
History of the human brain
Brain development
This development section covers changes in brain structure over time. It includes both the normal development of the human brain from infant to adult and genetic and evolutionary changes over many generations.
- Neural development in humans
- Neuroplasticity – changes in a brain due to behavior, environment, aging, injury etc.
- Nonsynaptic plasticity – changes in the axon, dendrites, and soma of individual neurons
- Parental brain – patterns in the brain of a new parent such as sensitivity towards infant cues, processing those cues and being motivated to engage with the infant
- Interpersonal relationship
- Cognitive genomics – genes and genome related to health and activity of the brain
- Neuroanthropology
Typical brain function
This section covers typical brain function as opposed to atypical function discussed below.
Sensory input
- Sense
- Sensory system
- Sensation (psychology)
- Sight
- Visual object recognition – the ability to visually perceive an object's physical properties
- Optic nerve (cranial nerve 2) – main sight-related cranial nerve
- Hearing
- Culture in music cognition – the impact that a person's culture has on their music cognition
- Aphasia – "speechlessness", a disturbance of the comprehension and formulation of language
- Cochlear nerve (part of cranial nerve 8) – the main hearing-related cranial nerve
- Smell
- Olfactory nerve (cranial nerve 1) – the main smell-related cranial nerve
- Taste
- Taste-related cranial nerves:
- Facial nerve (cranial nerve 7)
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (cranial nerve 9)
- Vagus nerve (cranial nerve 10)
- Taste-related cranial nerves:
- Somatosensory system
- Haptic perception
- Thermoception – sense of heat and coldness by the skin
- Proprioception – sense of the relative position of the parts of the body
- Nociception – signals pain in response to nerve-damage or damage to tissue
- Equilibrioception – sense of body movement, direction, acceleration, and balance
- Vestibular nerve (part of cranial nerve 8) – the main equilibrioception-related cranial nerve
- Peripheral chemoreceptor in the brain – monitors the carbon dioxide and oxygen levels in the brain
- Chemoreceptor trigger zone – area in the brain that receives inputs from drugs and hormones, and controls vomiting
- Reflex arc – neural pathway that controls an action reflex (activation of spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain)
Integration
- Functional integration – the hypothesis that the integration within and among specialized areas of the brain is mediated by effective connectivity
- Neurophilosophy – some observations on this type of approach and localization of function
- Receptor cell – cells that sense external stimuli and conducted that information to the brain
- Multisensory integration – organization of sensation from one's own body and the environment into usable functional outputs
- Lateralization of brain function
- Neurocomputational speech processing – computer-simulation of speech production and speech perception by referring to the natural neuronal processes
Affect
- Affective neuroscience
- Somatic marker hypothesis – postulate that emotional processes can guide behavior, particularly decision-making
Mind / body
- Philosophy of mind
- Body integrity identity disorder – when an individual feels they would be happier living as an amputee
- Phantom limb – when an individual has had a limb removed from the body but still receives sensory input from it
- Supernumerary phantom limb – when an individual receives sensory input from limbs of the body that never have existed
Memory
- Methods used to study memory – cumulation of evidence from human, animal, and developmental research in order to make broad theories about how memory works
- Chunking
- Object permanence
- Memory and aging
- Exceptional memory
- Memory disorder
- Eureka effect – the common human experience of suddenly understanding a previously incomprehensible problem or concept
- Muscle memory – the retention in the brain of memories of certain muscle movements, often enabling those specific movement to be duplicated in the future
- False memory
- Choice-supportive bias – the tendency to retroactively ascribe positive attributes to an option one has selected
- Fundamental attribution error – the tendency to overestimate the effect of disposition or personality and underestimate the effect of the situation in explaining social behavior
- Actor–observer asymmetry – discrepancy between attributions for one's own behavior and for that of others
- Reconstructive memory – theory that the act of remembering is influenced by various other cognitive processes including perception, imagination, semantic memory and beliefs
- Confabulation – a memory disturbance characterized by verbal statements or actions that inaccurately describe history, background, and present situations
- List of memory biases
Integration and cognition
- Sleep
- Neuroscience of sleep – the study of the neuroscientific and physiological basis of the nature of sleep and its functions
- Sleep and memory – memory processes have been shown to be stabilized and sped up by sleep. Certain sleep stages are noted to improve an individual's memory.
- Microsleep – an episode of sleep lasting from fraction of a second to thirty seconds
- Dreaming
- Abstraction – a process by which concepts are derived from the usage and classification of literal concepts
- Imagination – the ability to form new images and sensations that are not perceived through sight, hearing, or other senses
- Wakefulness
- Pre-attentive processing – the unconscious accumulation of information from the environment
- Preconscious – information that is available for cognitive processing but that currently lies outside conscious awareness
- Neural oscillation
- Resting state fMRI
- Default mode network – network of brain regions that are active when the individual is awake but not focused on the outside world
- Task-positive network – network of brain regions that are active during goal-oriented activity
- Attention
- Mindfulness
- Brain activity and meditation
- Research on meditation – a growing subfield of neurological research regarding what happens in the bodies and brains of people who meditate regularly
- Yoga-nidra – conscious awareness of the deep sleep state
Logic, computation, and information aspects
- Logic
- Cognitive neuropsychology
- Neuroinformatics – application of computational models and analytical tools to neuroscience
- Computational neuroscience
- Mind uploading – copying a brain state into a computer
- Bio-inspired computing
- Artificial intelligence
- Artificial neural network
- Artificial general intelligence – artificial intelligence that matches or exceeds human intelligence
- Natural computing – topics such as swarm intelligence, artificial immune systems, and artificial life
- Artificial intelligence
Executive function
- Supervisory attentional system – higher level system involved with elements of planning, inhibition, and abstraction of logical rules
- Metastability in the brain – the ability to make sense out of seemingly random environmental cues
- Neuroscience of free will – some actions are initiated and processed unconsciously at first, and only consciousnessly afterward
- Neuroeconomics – studying human decision making using techniques from neuroscience, psychology, and economics
- Neurophilosophy – exploration of the relevance of neuroscientific studies to the arguments traditionally categorized as philosophy of mind
- Neural basis of self – using modern concepts of neuroscience to describe a human's perception of self-understanding
- Mentalism (psychology) – branches of study that concentrate on mental perception and thought processes
- Animal cognition
- Lying
- Lie detection – questioning techniques and technologies to discern truth from falsehood
Motor output and behavior
- Motor skill – a learned sequence of movements that combine to produce a smooth, efficient action to master a particular task
- Muscle memory – the retention in the brain of memories of certain muscle movements, often enabling those specific movement to be duplicated in the future
- Behavioral neuroscience
Sexuality, sex differences, and gender differences
- Sex differences in human physiology § Brain
- Sex differences in human psychology
- Human sexuality
- Orgasm
- Infidelity – a breach of an expectation of sexual and or emotional exclusivity
- Neuroscience and sexual orientation
- Sexual desire
- Love
- Development
Higher level functioning
- Curiosity
- Interest
- Learning
- Linguistics
- Symbol
- Logic
- Mathematics
- Art
- Play
Atypical brain function
This section covers the major known deviations from typical brain functioning with an emphasis on the resulting magnitude of overall human suffering.
- Neurodegeneration – progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, including death of neurons
- Multiple sclerosis – inflammatory disease in which the myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged.
- Parkinson's disease – disease causing shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement and difficulty with walking and gait, followed by cognitive and behavioral problems and dementia
- Alzheimer's disease – the most common form of dementia, causing memory loss
- Huntington's disease – mutation in the huntingtin gene causing abnormal involuntary writhing movements, cognitive decline and psychiatric problems
- Dementia – abnormal loss of global cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person
- Brain cancer
- Brain metastasis – cancer that has spread to the brain from another location in the body
- Tuberous sclerosis – genetic disease that causes non-malignant tumors to grow in the brain and on other vital organs
- Brain damage
- Acquired brain injury
- Traumatic brain injury
- Stroke – rapid loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain
- Frontal lobe injury
- Coma
- Long-term disability and rehabilitation efforts:
- Cognitive rehabilitation therapy
- Rehabilitation (neuropsychology)
- Cognitive remediation therapy
- Drug
- Alcohol
- Disease theory of alcoholism – characterization of drinking problems by altered brain structure and function
- Long-term impact of alcohol on the brain
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome – vitamin B1 deficiency usually secondary to alcohol use, causing vision changes, ataxia, and impaired memory
- Alcoholic polyneuropathy – disorder resulting from alcoholism in which an individual experiences pain and motor weakness, first in the feet and hands and then progressing centrally
- Alcohol dependence
- Delirium tremens
- Alcoholic hallucinosis
- Short-term effects of alcohol consumption
- Cannabis
- Alcohol
- Gambler's fallacy – a cognitive bias and fallacy that arises out the erroneous belief that small samples must be representative of the larger population
- Mental disorder
- Acalculia – decrease in cognitive capacity for calculation resulting from damage to the brain
- CCK-4 – compound that reliably causes severe anxiety symptoms when administered to humans, commonly used in scientific research to induce panic attacks
- Thalamocortical radiations – fibers between the thalamus and the cerebral cortex, associated with activity which causes symptoms associated with impulse control disorders, Parkinson's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and other forms of chronic psychosis
- Treatment of mental disorders – treatments frequently mentioning brain dysfunction
- Epileptic seizure – transient symptom of abnormal excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain
Physical interventions
This section covers attempts to physically alter the brain state to relieve suffering, address atypical functioning or improve performance.
- Neurosurgery – surgery to the brain
- Specific procedures:
- Brain biopsy – removal of tissue from the brain to aid in diagnosis of disease
- Craniotomy
- Craterization
- Burr hole
- Trepanning
- Decompressive craniectomy
- Transsphenoidal surgery
- Intracranial pressure monitoring
- Psychosurgery – surgical treatment of mental disorders
- Specific regions frequently requiring surgery:
- Conditions frequently treated with surgery:
- Brain tumor
- Grading of the tumors of the central nervous system
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- Subdural hematoma
- Aneurysm
- Hydrocephalus
- Cerebral shunt
- Meningioma
- Pituitary adenoma – tumor in the pituitary gland
- Skull fracture
- Cranioplasty – correcting a defect or deformity of the skull
- Specific procedures:
- Radiation therapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery – multiple radiation beams converging at a tumor
- Chemotherapy – the use of drugs to kill or alter cancer cells
- Post-chemotherapy cognitive impairment – cognitive impairment that impacts 20–30% of people who undergo chemotherapy
- Electrotherapy
- Cortical stimulation mapping – direct electrical stimulation of the cerebral cortex to elicit a response
- Electroconvulsive therapy – psychiatric treatment in which seizures are electrically induced in anesthetized patients for potential therapeutic effect
- Neurobiological effects of physical exercise
Other
- Ten percent of brain myth
- Mobile phone radiation and health
- Neuroscience and intelligence
- Brain size – questions of links between weight or volume and intelligence
- Organization for Human Brain Mapping
- Common misconceptions about the brain
- Brain Mapping Foundation
Case histories
- Phineas Gage
- Gary Dockery
- Ahad Israfil
- KC
- Robert Lawrence
- Henry Molaison
- Terry Wallis
- Zasetsky
- Devin Galligan – underwent a special brain surgery whereby the patient is in a deep sleep during the first phase, but is awakened later later to perform a series of tests to help guide surgeons through the rugged pathways of the brain
- List of notable brain tumor patients
See also
External links
Human brain at Wikipedia's sister projects
 Definitions from Wiktionary
Definitions from Wiktionary Media from Commons
Media from Commons News from Wikinews
News from Wikinews Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote Texts from Wikisource
Texts from Wikisource Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks Resources from Wikiversity
Resources from Wikiversity
- Atlas of the Human Brain
- The Whole Brain Atlas
- High-Resolution Cytoarchitectural Primate Brain Atlases
- Brain Facts and Figures
- v
- t
- e
Wikipedia outlines
General reference
- Culture and the arts
- Geography and places
- Health and fitness
- History and events
- Mathematics and logic
- Natural and physical sciences
- People and self
- Philosophy and thinking
- Religion and belief systems
- Society and social sciences
- Technology and applied sciences

















