Methallyl chloride
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 3-Chloro-2-methylprop-1-ene | |
| Other names Isobutenyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.411 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2554 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula | C4H7Cl |
| Molar mass | 90.55 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.9210 g/cm3 (15 °C) |
| Boiling point | 71–72 °C (160–162 °F; 344–345 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
Pictograms |       |
| Danger | |
| H225, H302, H314, H317, H331, H335, H336, H351, H361, H372, H373, H411 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P310, P311, P312, P314, P321, P330, P333+P313, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | −12 °C (10 °F; 261 K) |
Autoignition temperature | 540 °C (1,004 °F; 813 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Chemical compound
Methallyl chloride is the organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)CH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid and a lacrymator. Its properties are similar to those of allyl chloride. It is a strong alkylating agent used to install isobutenyl groups.[1]
Reactivity
It is also a precursor to methallyl ligand. It is an isomer of crotyl chloride.
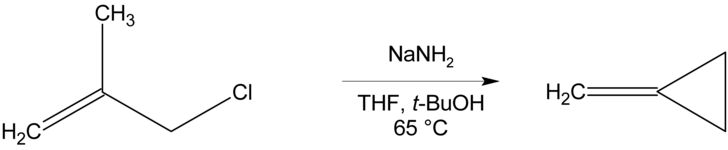
Methylenecyclopropane can be synthesised via an intramolecular cyclisation reaction from methallyl chloride by treatment with a strong base such as sodium amide.[2]
References
- ^ Krook, Mark A.; O'Doherty, George A.; Gao, Dong (2007). "Methallyl chloride". e-EROS Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–6. doi:10.1002/9780470842898.rm061.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ^ Salaun, J. R.; Champion, J.; Conia, J. M. (1977). "Cyclobutanone from Methylenecyclopropane via Oxaspiropentane". Organic Syntheses. 57: 36. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.057.0036.