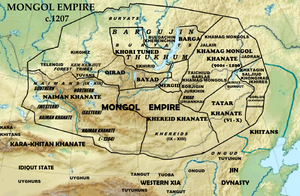
Khamag Mongol

EMPIRE
RUS'
CONFEDERATION
CALIPHATE
DYNASTY
DYNASTY
SULTANATE
OF RUM
RYEO
Mongolian Shamanism
(1st recorded Khan)
| Preceded by | Succeeded by | ||||||
|
|
Mongolia
Russia
Khamag Mongol (Mongolian: Хамаг монгол, romanized: Khamag mongol, lit. 'the whole Mongol'; Chinese: 蒙兀國) was a loose Mongolic tribal confederation (khanlig) on the Mongolian Plateau in the 12th century. It is sometimes considered to be a predecessor state to the Mongol Empire.[2][3]
The existence of a somewhat mysterious tribal power known in Mongol tradition as Khamag Mongol Uls is recorded in sources of the Khitan-led Liao dynasty.[4] After the fall of the Liao dynasty in 1125, the Khamag Mongols began to play an important role on the Mongolian plains.[5] They occupied one of the most fertile lands of the country, the basins of the river Onon, Kherlen and Tuul Rivers in the Khentii Mountains. The Taichiud (Cyrillic: Тайчууд) was one of the three core tribes in the Khamag Mongol Khanate of Mongolia during the 12th century and whose people lived in the southern part of Siberia's modern-day Zabaykalsky Krai. The present-day Zabaykalsky Krai and the Khentii Province of Mongolia were the core regions of the Khamag Mongol Khanate.[6] The Khamags consisted of the three core clans Khiyad, Taichuud, and Jalairs.
The first khan of Khamag Mongol recorded in history is Khabul Khan from the Borjigin clan. Khabul Khan successfully repelled the invasions of the Jurchen-led Jin armies. Khabul Khan was succeeded by Ambaghai Khagann of the Taichiud. Ambagai was captured by the Tatar confederation while delivering his daughter for marriage to their leadership. He was handed over to the Jin, who cruelly executed him. Ambaghai was succeeded by Hotula Khan, a son of Khabul Khan. Hotula Khan engaged the Tatars in 13 battles in an effort to obtain vengeance for the death of Ambagai Khan.
Khamag Mongol was unable to elect a khan after Hotula died. However, Khabul's grandson Yesugei, who was a chief of the Khiyad tribe, was an effective and preeminent leader of Khamag Mongol. Temujin, the future Genghis Khan, was born into Yesugei's family as the first son in Delüün Boldog on the upper reaches of the Onon river in 1162.
When young Tughril Khan asked for help from Yesugei, the ruler of the Khamag Mongol,[note 1] to dethrone his brothers among the Keraites, the Mongols helped him defeat the Keraite leaders and put him on the throne in the early 12th century.
Yesugei was poisoned by the Tatars and died shortly after in 1171, after which the Khamag Mongol began to disintegrate. Political anarchy and a power vacuum lasted until 1189 when Temujin became the Khan of the Khamag Mongol. War broke soon out between other Mongol tribes. Temujin's friend Jamukha was recognized by the rival tribes as Gurkhan (the universal ruler) in 1201 but he was defeated by the alliance of Khamag Mongol and Keraites.
When Tughril Khan refused to cement the alliance with the Khamag, Temujin's wars with the clans nearly destroyed him. Temujin united all clans on the Mongolian Plateau at last in 1206, when he was given the title Genghis Khan.
See also
Notes
References
Citations
- ^ Journal Smith, John Masson (1975). "Mongol Manpower and Persian Population". Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient. 18 (3): 271–299. doi:10.2307/3632138. ISSN 0022-4995.
- ^ Bat-Ocher Bold (2001), Mongolian nomadic society: a reconstruction of the "medieval" history of Mongolia, Richmond, Surrey: Curzon, p. 176, ISBN 0-7007-1158-9
- ^ History of the Mongolian People's Republic By Akademii︠a︡ nauk SSSR, p. 99.
- ^ Khamag Mongol Uls
- ^ Histoire de la Mongolie By László Lőrincz, p. 43.
- ^ History of Mongolia, Volume II, 2003
Sources
- Akademiiya nauk SSSR – History of the Mongolian People's Republic, Nauka Pub. House, Central Dept. of Oriental Literature, 1973
- Bat-Ochir Bold – Mongolian Nomadic Society, St. Martin's Press, 1999. ISBN 0-312-22827-9
- The New Encyclopædia Britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, 1974: Macropaedia Me-Ne ISBN 0-85229-290-2
- László Lőrincz – Histoire de la Mongolie, Akadémiai Kiadó,the University of Michigan, 1984. ISBN 963-05-3381-2












