Isobutyl nitrite
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-Methylpropyl nitrite | |||
| Other names Isobutyl nitrite | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
| ||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.018 | ||
PubChem CID |
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
| ||
InChI
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula | C4H9NO2 | ||
| Molar mass | 103.11976 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | Almond-like[2] | ||
| Density | 0.87 g/mL | ||
| Boiling point | 67 °C (153 °F; 340 K) | ||
Solubility in water | Slightly soluble | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards | Highly flammable | ||
| Legal status | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).  Y verify (what is Y verify (what is  Y Y N ?) N ?) Infobox references | |||
Chemical compound
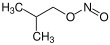
Isobutyl nitrite, C4H9NO2, is an alkyl nitrite, an ester of isobutanol and nitrous acid. Its chemical structure is (CH3)2CH-CH2-ONO.
Isobutyl nitrite is a pungent colorless liquid. It acts as a vasodilator, and is used as an inhalant recreational drug, poppers.
Applications
Isobutyl nitrite is one of the compounds used as poppers, an inhalant drug that induces a brief euphoria. Also, it is used as part of the antidote package for cyanide poisoning.[medical citation needed]
Safety
May cause headaches, dizziness and fainting. Isobutyl nitrite is poisonous to people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.[4]
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 5032.
- ^ CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
- ^ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- ^ Bubp, Jeff; Jen, Marilyn; Matuszewski, Karl (September 2015). "Caring for Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD)–Deficient Patients: Implications for Pharmacy". Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 40 (9): 572–574. ISSN 1052-1372. PMC 4571844. PMID 26417175.
- v
- t
- e
- Nitroxyl anion (NO−; oxonitrate(1-), hyponitrite anion)
- Nitric oxide (NO⋅; nitrogen monoxide)
- Nitrosonium (NO+; nitrosyl cation)
| sGC |
|
|---|
(prodrugs)
- Nitrates: Diethylene glycol dinitrate (DEGDN)
- Erythritol tetranitrate (ETN)
- Ethylene glycol dinitrate (EGDN; nitroglycol)
- Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN)
- Isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN)
- Itramin tosilate
- Mannitol hexanitrate
- Naproxcinod (nitronaproxen; AZD-3582, HCT-3012)
- NCX-466
- NCX-2216
- NCX-4016
- NCX 4040
- NCX-4215
- Nicorandil
- Nipradilol (K-351)
- Nitrate (NO−
3) - Nitroatorvastatin (NCX-6560)
- Nitroflurbiprofen (HCT-1026)
- Nitrofluvastatin
- Nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate (GTN))
- Nitropravastatin (NCX-6550)
- Pentaerithrityl tetranitrate (PETN)
- Propatylnitrate
- Propylene glycol dinitrate (PGDN)
- Sodium trioxodinitrate (Angeli's salt)
- Tenitramine
- Trolnitrate
- Nitroso compounds/nitrites: Nitrite (NO−
2); O-Nitroso compounds (alkyl nitrites): Amyl nitrite (isoamyl nitrite, isopentyl nitrite) - Cyclohexyl nitrite
- Ethyl nitrite
- Hexyl nitrite
- Isobutyl nitrite (2-methylpropyl nitrite)
- Isopropyl nitrite
- Methyl nitrite
- n-Butyl nitrite
- Pentyl nitrite
- tert-Butyl nitrite; S-Nitroso compounds (thionitrites): LA810
- S-Nitrosoalbumin (SNALB)
- S-Nitrosated AR545C
- S-Nitroso-N-acetylcysteine (SNAC)
- S-Nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP)
- S-Nitroso-N-valerylpenicillamine (SNVP)
- S-Nitrosocaptopril (SNO-Cap)
- S-Nitrosocysteine (SNC, CysNO, SNO-Cys)
- S-Nitrosodiclofenac
- S-Nitrosoglutathione (GSNO, SNOG)
- SNO-t-PA
- SNO-vWF; N-Nitroso compounds (e.g., nitrosamines): SIN-1A
- Nitrosyl compounds: Metal nitrosyl complexes: Roussin's black salt
- Roussin's red salt
- Sodium nitroprusside (SNP)
- NONOates (diazeniumdiolates): Diethylamine/NO (DEA/NO)
- Diethylenetriamine/NO (DETA/NO)
- GLO/NO
- JS-K
- Methylamine hexamethylene methylamine/NO (MAHMA/NO)
- PROLI/NO
- Spermine/NO (SPER/NO)
- V-PYRRO/NO
- Heterocyclic compounds: Furoxans: Furoxan
- REC15/2739; Sydnonimines: Feprosidnine
- Linsidomine (SIN-1)
- Molsidomine (SIN-10)
- Sydnonimine
- Unsorted: Cimlanod
- FK-409
- FR144220
- FR146881
- N-Acetyl-N-acetoxy-4-chlorobenzenesulfonamide
(inhibitors)
| NOS |
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arginase |
| ||||||||
| CAMK |
|
- Precursors: L-Arginine
- Nω-Hydroxy-L-arginine (NOHA)
- Indirect/downstream NO modulators: ACE inhibitors/AT-II receptor antagonists (e.g., captopril, losartan)
- ETB receptor antagonists (e.g., bosentan)
- L-Type calcium channel blockers (e.g., dihydropyridines: nifedipine)
- Nebivolol (beta blocker)
- PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil)
- non-selective PDE inhibitors (e.g., caffeine)
- PDE9 inhibitors (e.g., paraxanthine)
- cGMP preferring PDE inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, paraxanthine, tadalafil)
- Statins (e.g., simvastatin)
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators
 | This psychoactive drug-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e