Diboron tetrafluoride
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Diboron tetrafluoride | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name Tetrafluorodiborane(4) | |||
| Identifiers | |||
CAS Number |
| ||
3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ChemSpider |
| ||
PubChem CID |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
| ||
InChI
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
Chemical formula | B2F4 | ||
| Molar mass | 97.61 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless gas | ||
| Density | 4.3 kg/m3 (gas) | ||
| Melting point | −56 °C (−69 °F; 217 K) | ||
| Boiling point | −34 °C (−29 °F; 239 K) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C) | 79.1 J/mol K | ||
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 317.3 J/mol K | ||
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -1440.1 kJ/mol | ||
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵) | -1410.4 kJ/mol | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
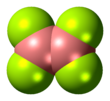
Diboron tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula (BF2)2. A colorless gas, the compound has a halflife of days at room temperature. It is the most stable of the diboron tetrahalides,[1] and does not appreciably decompose under standard conditions.[2]
Structure and bonding
Diboron tetrafluoride is a planar molecule with a B-B bond distance of 172 pm.[1] Although it is electron-deficient, the unsaturated boron centers are stabilized by pi-bonding with the terminal fluoride ligands. The compound is isoelectronic with oxalate.
Synthesis and reactions
Diboron tetrafluoride can be formed by treating boron monofluoride with boron trifluoride at low temperatures, taking care not to form higher polymers.[3] Alternatively, diboron tetrachloride can be fluorinated with antimony trifluoride.[2]
Addition of diboron tetrafluoride to Vaska's complex was employed to produce an early example of a transition metal boryl complex:[4]
- 2 B2F4 + IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2 → Ir(BF2)3(CO)(PPh3)2 + ClBF2
Historical literature
- Louis Trefonas and William N. Lipscomb (1958). "Crystal and Molecular Structure of Diboron Tetrafluoride, B2F4". J. Chem. Phys. 28 (1): 54–55. Bibcode:1958JChPh..28...54T. doi:10.1063/1.1744079.
- Gayles, J. N.; Self, J. (1964). "Infrared Spectrum of Diboron Tetrafluoride in the Gaseous and Solid States". Journal of Chemical Physics. 40 (12): 3530–3539. Bibcode:1964JChPh..40.3530G. doi:10.1063/1.1725048.
- A. K. Holliday; F. B. Taylor (1964). "Diboron tetrafluoride. Part II. Reactions with some oxides and organometallic compounds". J. Chem. Soc.: 2731–2734. doi:10.1039/JR9640002731.
- Vernon H. Dibeler; Susan K. Liston (1968). "Mass-spectrometric study of photoionization. XII. Boron trifluoride and diboron tetrafluoride". J. Chem. Soc. 7 (9): 1742–1746. doi:10.1021/ic50067a010.
References
- ^ a b Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b Arthur Finch and Hermann Irving Schlesinger (1958). "Diboron Tetrafluoride". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 80 (14): 3573–3574. doi:10.1021/ja01547a020.
- ^ Timms, P. L. (1972). "Low Temperature Condensation of High Temperature Species as a Synthetic Method". Advances in Inorganic Chemistry and Radiochemistry. Academic Press: 143. doi:10.1016/S0065-2792(08)60006-0. ISBN 0-12-023614-1.
- ^ Neeve, Emily C.; Geier, Stephen J.; Mkhalid, Ibraheem A. I.; Westcott, Stephen A.; Marder, Todd B. (2016). "Diboron(4) Compounds: From Structural Curiosity to Synthetic Workhorse". Chemical Reviews. 116 (16): 9091–9161. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00193. hdl:1807/78811. PMID 27434758.
External links
- Diboron tetrafluoride at webelements
- v
- t
- e
- B(NO3)3
- B(OH)3
- BPO4
- BH3
- B2H4
- B2H6
- BH3NH3
- B4H10
- B5H9
- B5H11
- B6H10
- B6H12
- B10H14
- B18H22
- B2O
- B2O3
- B2S3
- B6O
- B4C
- (BH2Me)2
- BMe3
- BEt3
- Ac4(BO3)2
- COBH3