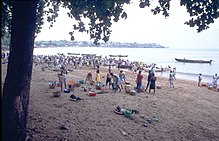Cuisine of São Tomé and Príncipe



Santomean cuisine comprises the cuisine, dishes and foods of São Tomé and Príncipe, a Portuguese-speaking island nation in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. The country consists of two archipelagos around the two main islands: São Tomé and Príncipe, located about 140 kilometres (87 mi) apart and about 250 and 225 kilometres (155 and 140 mi), respectively, off the northwestern coast of Gabon.
Overview
Domestic food-crop production is inadequate to meet local consumption, so the country imports much of its food.[1] In 1997, it was estimated that 90 percent of the country's food needs were met through imports[1] including meat and food-grains.[1] In 2003, it was estimated that 8.33% of the country's total land is arable.[2]
Primary food crops include bananas, breadfruit, taro, maize, beans, papaya, palm oil, and primary agricultural production crops for export include cocoa, copra and coffee.[1][3] Fish and seafood is prominent in São Tomése and Príncipe cuisine, and the fishing industry contributes approximately 25 percent to the country's gross domestic product.[1][4] Poultry is also raised in São Tomé and Príncipe.[1]
The nation's cuisine has been influenced and shaped by African and Portuguese settlers.[5]
Common foods
Staple foods include fish, seafood, beans, maize and cooked banana.[4][6] Tropical fruits such as pineapple, avocado and bananas are a significant component of the cuisine.[4] The use of hot spices is prominent in São Tomése cuisine.[4] Coffee is utilized in various dishes as a spice or seasoning.[4] Breakfast dishes are often reheated leftovers from the previous evening's meal.[6]
- Arroz doce (rice pudding) is a traditional breakfast food prepared with sweet corn and coconut[6]
- Banana pap is a porridge[5]
- Barriga de peixe is a traditional Santomean dish of grilled fish served with rice, breadfruit or manioc (cassava)[6]
- Blablá[clarification needed][6]
- Broa—cornmeal and rye bread[6]

- Cachupa is a dish prepared with green beans, broad beans and corn.[6]
- Calulu is a traditional dish prepared with grouper or smoked fish, prawns, tomato, okra, aubergines (eggplant), onion, and spices, including grains of paradise.[4][6] Some versions of the dish may include or use smoked chicken, breadfruit, óssame (a red, bulbous fruit) or bananas.[6] It takes around five hours for traditional calulu to be prepared.[6] Variations of callaloo are eaten in other countries
- Chicken
- Chicken with coffee sauce is prepared with chicken, coffee, white wine, cream, garlic, coffee beans and spices[4]
- Coconut
- Djogo[clarification needed] [6]
- Flying fish, both cooked and dried varieties[6]
- Jackfruit[6]
- Mango[6]
- Omelettes [6]
- Boiled pork is a dish prepared with pork, tomato, spinach, onion, garlic and spices[4]
-
 Jackfruit being prepared for consumpution
Jackfruit being prepared for consumpution -
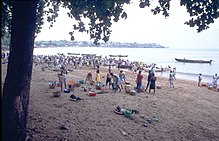 Fishermen land their catch of fish in Sao Tomé.
Fishermen land their catch of fish in Sao Tomé. -
 Shrimp and French fries as served in a local hotel, São Tomé
Shrimp and French fries as served in a local hotel, São Tomé


- Safu, short of safous, is the Dacryodes edulis fruit
Beverages

- Carioca de limão is prepared with lemon peel and hot water.[6]
- Coconut water[6]
- Coffee[6]
- Soft drinks [6]
- Tea[6]
Alcoholic beverages
- Aquardente is a distilled beverage prepared from sugar cane.[6]
- Nacional is the country's national beer.[6] Other beers, such as Super Bock and Sagres lager are imported from Portugal.[6] Criollo is another brand of beer produced in the country.[6]
- Gravana rum is prepared from sugar cane.[6]
- Palm wine is considered a national drink of São Tomé and Príncipe.[6]
- Ponche is a cocktail prepared with honey and Aquardente.[6]
- Wines, typically imported from Portugal[6]
Street foods

Street foods include stews, safú (a fruit) and corn on the cob.[6]
Delicacies
Estufa de morcego is a bat stew delicacy that is served on saints days and during fiestas.[6]
Desserts and sweets
- Açucarinhas are prepared from coconut and sugar, formed into patties, and fried in palm oil.[6]
- Aranha is prepared with coconut, sugar strings and food coloring.[6]
- Canjica is a porridge that is prepared with canjica maize kernels, egg, sugar, cinnamon and water.[4][5]
- Chocolate
- Chocolate mousse[6]

Snack foods
- Banana seca is a dried, whole banana that has a smoky flavor.[6]
- Bobofrito is a specialty of Príncipe that consists of bananas fried in coconut oil.[6]
- Bread rolls with Portuguese salami and sausages[5]
- Fios is a snack food prepared with corn flour and bananas.[6]
- Gigumba (peanut brittle) [6]
- Palla-palla are crisps prepared with cocoyam or banana.[6]
Condiments
- Piri-piri sauce prepared with malagueta pepper is commonly available in Santomean restaurants.[6]
See also
References
- ^ a b c d e f Agricultural Marketing Directory for U.S. & Africa Trade - Mary E. Lassanyi, Wayne Olson. p. 206.
- ^ "São Tomé and Príncipe: Agriculture". NationMaster. Archived from the original on 23 February 2014. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- ^ Sao Tomé and Príncipe - Recent Economic Developments and Selected Issues (EPub) - International Monetary Fund. p. 70.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i The Recipes of Africa – Dyfed Lloyd Evans. pp. 174-176.
- ^ a b c d São Tomé. Foodspring. Accessed February 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an Sao Tome and Principe – Kathleen Becker. pp. 74-79.
Further reading
- Weinberg, Samantha (April 2013). "Chocolate and Slavery". Intelligent Life magazine (The Economist). Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- Rice, Xan (January 15, 2009). "The chocolate king of São Tomé". New Statesman. Retrieved 8 February 2014.
- Democratic Republic of Sao Tome and Principe: Request for a Three-Year Arrangement Under the Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility. International Monetary Fund. pp. 4–5.
External links
- v
- t
- e
- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Eswatini (Swaziland)
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Ivory Coast
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Republic of the Congo
- Rwanda
- Saint Helena
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Western Sahara
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
 Category
Category