Ancient Southern East Asian

In archaeogenetics, Ancient Southern East Asian (ASEA), also known as Southern East Asian (sEA), is an ancestral lineage that is represented by individuals from Qihe Cave in Fujian (c. 12–8 kya) and Liangdao Island in the Taiwan Strait (c. 8 kya) as well as Guangxi (c. 9 kya). Ancient Southern East Asian ancestry significantly contributed to the genetic makeup of modern populations in East Asia, Mainland Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia, and Oceania, and is commonly associated with the Neolithic expansion of early Austronesian and Austroasiatic speakers that occurred more than 4,000 years ago.
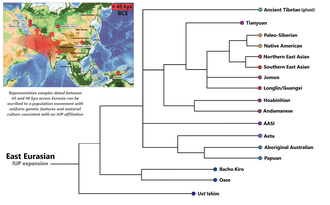
Origins
Until the early Holocene, Ancient Southern East Asians from Fujian were genetically clearly distinct from Ancient Northern East Asians (ANEA) who were distributed in an area stretching from the Yellow River to the Amur. The exact origins of both lineages is still only partially understood, but together they formed a distinct clade vis-a-vis all other known ancient East Eurasian lineages in eastern Asia, viz. the Tianyuan, Hoabinhian, Jomon, and Guangxi/Longlin ancestries.[1][2] The split between the ASEA and ANEA lineages must have occurred at least 19,000 years ago, as evidenced by an 19ky-old Upper Pleistocene individual from the Amur river with a clear ANEA affinity.[3]
In the mid-Holocene, southward migrations of millet farmers from the Yellow River harboring ANEA ancestry (and also to lesser degree a reverse geneflow of ASEA rice farmers from the Yangtse River to the north) resulted in the coastal East Asian ancestry cline that exists to this day. Northern Han Chinese mostly carry ANEA ancestry with a moderate degree of ASEA admixture, whereas southern Han Chinese as well as non-Han ethnic groups of southern East Asia (viz. speakers of Kra-Dai and Hmong-Mien languages) still carry significantly higher levels of ASEA ancestry.[4][5]
Neolithic expansion into Southeast Asia and Oceania

Starting from the third millennium BCE, rice farming-based agriculture spread from southern East Asia into Mainland and Insular Southeast Asia. This technological spread was a result of the migration of southern East Asian agriculturalists that carried ASEA ancestry. These Neolithic farmers took two routes: an inland route into Mainland Southeast Asia, and an maritime route that originated from Taiwan.[6][5][7]
Ancient DNA of first farmer individuals from Mainland Southeast Asia dated at c. 4kya derives most of its ancestry from the ASEA lineage, with significant admixture from a local hunter-gatherer population.[a] This Neolithic Mainland Southeast Asian ancestry peaks among modern populations in Austroasiatic-speaking groups of Southeast Asia (most notably in the Mlabri and Htin peoples in northern Laos and Thailand) and parts of East Asia and South Asia. Hence, the first spread of farming in Mainland Southeast Asia is widely assumed to be linked to the expansion of the Austroasiatic languages.[8][6] From Mainland Southeast Asia, this Austroasiatic-related ancestry spread into Insular Southeast Asia to the Sunda Islands,[8] adjacent areas (viz. Palawan, Mindanao) of the Philippines,[11] and western Wallacea,[12][13] although there are no remaining Austroasiatic languages spoken in this area, having been supplanted by incoming Austronesian languages.
The rapid maritime expansion of the early Austronesians starting c. 5,000–4,000 years ago brought ASEA ancestry from Taiwan to the Philippines, the Indonesian archipelago and Oceania, initially with little admixture from local populations, as can be seen from 2,900–2,500 year-old Lapita-related individuals from Vanuatu and Tonga,[14] and from ancient 2,800–2,200 year-old DNA of the first settlers of Guam.[15] In western Indonesia, Austronesian settlers admixed with people from the Austroasiatic-related settlement stream with Neolithic Mainland Southeast Asian ancestry,[5] while in eastern Indonesia and Oceania, all Austronesian-speaking groups have Papuan-related geneflow at various levels.[14][12][15] Later migrations of Austronesian speakers brought ASEA ancestry as far as to Madagascar and eastern Polynesia.[6]
Notes
- ^ Local hunter-gatherer contributed around 30% to the Neolithic Mainland Southeast Asian genepool.[8] A potential source for the local pre-Neolithic component is the Hoabinhian lineage represented by two individuals from Laos and Malaysia,[9][6][5] whose ancestry still persists at high levels in the Semang hunter-gatherers of Malaysia and southern Thailand.[9] An alternative source represents the Guangxi/Longlin lineage, represented by a specimen found in modern day Guangxi.[10]
References
- ^ Zhang & Fu 2020, p. 81.
- ^ Yang 2022, pp. 14, 17.
- ^ Mao et al. 2021, p. 3260.
- ^ Yang et al. 2020, pp. 5–6.
- ^ a b c d Zhang & Fu 2020, p. 82.
- ^ a b c d Stoneking et al. 2023, p. 5.
- ^ Nägele et al. 2022, p. 207–208.
- ^ a b c Lipson et al. 2018.
- ^ a b McColl et al. 2018.
- ^ Wang et al. 2021.
- ^ Larena et al. 2021.
- ^ a b Oliveira et al. 2022.
- ^ Stoneking et al. 2023, p. 5–6.
- ^ a b Stoneking et al. 2023, p. 6.
- ^ a b Liu et al. 2022, p. 6.
Bibliography
- Larena, Maximilian; Sanchez-Quinto, Federico; Sjödin, Per; McKenna, James; et al. (2021). "Multiple migrations to the Philippines during the last 50,000 years". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 118 (13). Bibcode:2021PNAS..11826132L. doi:10.1073/pnas.2026132118. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 8020671. PMID 33753512.
- Lipson, Mark; Cheronet, Olivia; Mallick, Swapan; Rohland, Nadin; et al. (2018). "Ancient genomes document multiple waves of migration in Southeast Asian prehistory". Science. 361 (6397): 92–95. Bibcode:2018Sci...361...92L. doi:10.1126/science.aat3188. ISSN 0036-8075. PMC 6476732. PMID 29773666.
- Liu, Yue-Chen; Hunter-Anderson, Rosalind; Cheronet, Olivia; Eakin, Joanne; et al. (2022). "Ancient DNA reveals five streams of migration into Micronesia and matrilocality in early Pacific seafarers". Science. 377 (6601): 72–79. Bibcode:2022Sci...377...72L. doi:10.1126/science.abm6536. PMC 9983687. PMID 35771911.
- Mao, Xiaowei; Zhang, Hucai; Qiao, Shiyu; Liu, Yichen; et al. (2021). "The deep population history of northern East Asia from the Late Pleistocene to the Holocene". Cell. 184 (12): 3256–3266.e13. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.040. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 34048699. S2CID 235226413.
- McColl, Hugh; Racimo, Fernando; Vinner, Lasse; Demeter, Fabrice; et al. (2018). "The prehistoric peopling of Southeast Asia". Science. 361 (6397). American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS): 88–92. Bibcode:2018Sci...361...88M. doi:10.1126/science.aat3628. hdl:10072/383365. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 29976827. S2CID 206667111.
- Nägele, Kathrin; Rivollat, Maite; Yu, He; Wang, Ke (2022). "Ancient genomic research - From broad strokes to nuanced reconstructions of the past". Journal of Anthropological Sciences. 100 (100): 193–230. doi:10.4436/jass.10017. PMID 36576953.
- Oliveira, Sandra; Nägele, Kathrin; Carlhoff, Selina; Pugach, Irina; et al. (2022). "Ancient genomes from the last three millennia support multiple human dispersals into Wallacea". Nature Ecology & Evolution. 6 (7): 1024–1034. Bibcode:2022NatEE...6.1024O. doi:10.1038/s41559-022-01775-2. PMC 9262713. PMID 35681000.
- Stoneking, Mark; Arias, Leonardo; Liu, Dang; Oliveira, Sandra; et al. (2023). "Genomic perspectives on human dispersals during the Holocene". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 120 (4): e2209475119. Bibcode:2023PNAS..12009475S. doi:10.1073/pnas.2209475119. ISSN 1091-6490. PMC 9942792. PMID 36649433.
- Wang, Chuan-Chao; Yeh, Hui-Yuan; Popov, Alexander N.; Zhang, Hu-Qin; et al. (2021). "Genomic insights into the formation of human populations in East Asia". Nature. 591 (7850): 413–419. Bibcode:2021Natur.591..413W. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03336-2. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 7993749. PMID 33618348.
- Yang, Melinda A.; Fan, Xuechun; Sun, Bo; Chen, Chungyu; et al. (2020). "Ancient DNA indicates human population shifts and admixture in northern and southern China". Science. 369 (6501): 282–288. Bibcode:2020Sci...369..282Y. doi:10.1126/science.aba0909. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 32409524. S2CID 218649510.
- Yang, Melinda A. (2022). "A genetic history of migration, diversification, and admixture in Asia". Human Population Genetics and Genomics. 2 (1): 1–32. doi:10.47248/hpgg2202010001. ISSN 2770-5005.
- Zhang, Ming; Fu, Qiaomei (2020). "Human evolutionary history in Eastern Eurasia using insights from ancient DNA". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 62: 78–84. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2020.06.009. ISSN 0959-437X. PMID 32688244. S2CID 220671047.
- Wang, Tianyi; Wang, Wei; Xie, Guangmao; Li, Zhen; Fan, Xuechun; Yang, Qingping; Wu, Xichao; Cao, Peng; Liu, Yichen; Yang, Ruowei; Liu, Feng; Dai, Qingyan; Feng, Xiaotian; Wu, Xiaohong; Qin, Ling (8 July 2021). "Human population history at the crossroads of East and Southeast Asia since 11,000 years ago". Cell. 184 (14): 3829–3841.e21. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.018. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 34171307.










